Understanding the Role of Vacuum Pump Suppliers in the United States Industrial Landscape
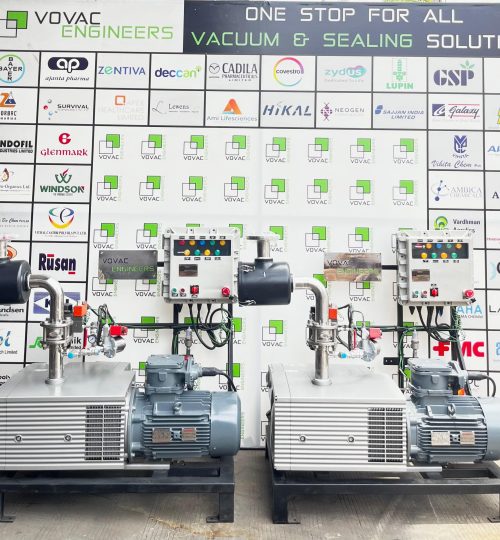

Vacuum technology is a foundational component of many industries in the United States, supporting processes that require controlled pressure environments. From manufacturing and research to food processing and healthcare, vacuum systems enable precision, efficiency, and safety. Within this broader ecosystem, the term vacuum pump suppliers is commonly used to describe organizations involved in providing, distributing, and supporting vacuum pump equipment and related services. Understanding this term involves examining the functions these suppliers serve, the industries they support, and the technical and logistical considerations associated with vacuum systems.
Rather than referring to a single company or product, vacuum pump suppliers collectively represent a segment of the industrial supply chain that connects manufacturers of vacuum technology with end users. Their role extends beyond simple distribution and often includes technical guidance, system integration support, and ongoing equipment servicing.
Overview of Vacuum Pump Technology
Vacuum pumps are mechanical devices designed to remove gas molecules from a sealed space, thereby creating a vacuum or low-pressure environment. Different types of vacuum pumps are used depending on the level of vacuum required, the nature of the gases involved, and the application environment. Common categories include rotary vane pumps, dry vacuum pumps, diaphragm pumps, scroll pumps, and turbomolecular pumps.
Because each type has specific operating characteristics, selecting the appropriate pump requires technical understanding. Vacuum pump suppliers often operate at the intersection of engineering knowledge and practical application, helping match equipment specifications with process requirements.
Industries Served by Vacuum Pump Suppliers
In the United States, vacuum pump suppliers support a wide range of industries. Manufacturing sectors such as electronics, automotive, and aerospace rely on vacuum systems for processes like coating, molding, and material handling. In the semiconductor industry, vacuum environments are essential for fabrication and contamination control.
Healthcare and life sciences also depend on vacuum technology. Applications include laboratory research, pharmaceutical production, sterilization, and medical device manufacturing. Food and packaging industries use vacuum systems for preservation, sealing, and quality control. Across these sectors, vacuum pump suppliers play a role in ensuring that appropriate equipment is available and maintained.
Scope of Services Provided
The term vacuum pump suppliers encompasses more than the act of supplying equipment. Many suppliers also provide application-specific guidance, helping users understand system requirements such as vacuum level, flow rate, and compatibility with process gases. This consultative role is particularly important in complex or regulated environments.
In addition to equipment provision, suppliers may support installation coordination, maintenance planning, and access to replacement components. While not all suppliers offer the same level of service, the broader category includes organizations involved in various stages of the equipment lifecycle.
Technical Considerations in Vacuum Pump Supply
Supplying vacuum pumps involves addressing several technical considerations. One of the primary factors is vacuum range, which refers to the pressure level the pump can achieve. Different applications require rough vacuum, medium vacuum, or high vacuum conditions, and not all pumps are suitable for every range.
Another key consideration is process compatibility. Certain applications involve corrosive, reactive, or particulate-laden gases. Vacuum pump suppliers must account for material compatibility and design features that allow pumps to operate safely and reliably under these conditions.
Operating environment also influences pump selection. Factors such as ambient temperature, duty cycle, noise limitations, and available utilities can affect performance. Suppliers often help navigate these variables to ensure that the selected equipment aligns with operational constraints.
Supply Chain and Availability Factors
Vacuum pump suppliers operate within a broader supply chain that includes manufacturers, component providers, logistics networks, and end users. In the United States, supply chain dynamics can influence equipment availability, lead times, and maintenance planning.
Fluctuations in raw material supply, transportation capacity, and global manufacturing trends can affect how quickly pumps and parts are delivered. As a result, suppliers often manage inventory strategies and coordinate with multiple stakeholders to meet demand. These logistical considerations are an important but less visible aspect of the supplier role.
Replacement Parts and Lifecycle Support
Vacuum pumps are long-term investments, and their performance depends on regular maintenance and timely replacement of wear components. Vacuum pump suppliers are often involved in providing access to seals, filters, bearings, and other consumable parts required for ongoing operation.
Lifecycle support may also include guidance on refurbishment, performance evaluation, or end-of-life considerations. By supporting maintenance and repair activities, suppliers help extend equipment lifespan and maintain process reliability.
Role in Compliance and Standards
Many industries in the United States operate under regulatory frameworks that influence equipment selection and operation. Vacuum systems used in pharmaceutical production, food processing, or medical applications may need to comply with specific standards related to cleanliness, safety, or documentation.
Vacuum pump suppliers often need to understand these regulatory contexts to ensure that supplied equipment meets applicable requirements. While suppliers are not regulators, their familiarity with standards can help users navigate compliance-related considerations during system planning and operation.
Customization and System Integration
In some applications, standard vacuum pumps may not fully meet process needs. Customization or system integration may be required to achieve desired performance. This can involve combining pumps with accessories such as filters, traps, controls, or monitoring systems.
Vacuum pump suppliers may participate in these integration efforts by coordinating components or advising on system configuration. This role highlights how suppliers function not just as equipment sources but as contributors to system-level solutions.
Technological Trends Influencing Suppliers
Advancements in vacuum technology continue to shape the role of vacuum pump suppliers. Trends such as increased use of dry vacuum systems, digital monitoring, and energy-efficient designs influence how equipment is selected and supported.
As end users adopt more data-driven maintenance and monitoring practices, suppliers may be involved in providing compatible equipment or technical information. These evolving expectations contribute to changes in how suppliers interact with customers and manage technical knowledge.
Environmental and Energy Considerations
Energy consumption and environmental impact are growing concerns across many industries. Vacuum pumps can be significant energy users, particularly in continuous-operation settings. Vacuum pump suppliers must consider efficiency characteristics when matching equipment to applications.
Environmental considerations may also include handling of exhaust gases, noise levels, and waste management associated with maintenance. Suppliers often address these factors as part of broader discussions about system performance and sustainability.
Challenges Faced by Vacuum Pump Suppliers
Vacuum pump suppliers in the United States face several challenges, including rapid technological change, fluctuating demand across industries, and the need to maintain technical expertise. Workforce training and knowledge retention are ongoing concerns, especially as systems become more complex.
Economic factors such as market cycles and capital investment trends also influence supplier operations. During periods of industrial expansion, demand for vacuum systems may increase, while economic slowdowns can reduce capital spending. Suppliers must adapt to these conditions while maintaining service capabilities.
Importance of Information and Education
Because vacuum systems are highly application-specific, accurate information and education play a significant role in the work of vacuum pump suppliers. Clear communication about specifications, operating limits, and maintenance requirements helps ensure that equipment is used effectively.
Educational materials, technical documentation, and training resources are often part of the broader ecosystem associated with vacuum pump suppliers. These resources support informed decision-making and contribute to safer, more reliable operation.
Conclusion
The keyword vacuum pump suppliers represents an essential component of the industrial and technological infrastructure in the United States. These suppliers connect vacuum technology with the diverse applications that depend on controlled pressure environments, spanning manufacturing, healthcare, research, and beyond.
Understanding vacuum pump suppliers involves recognizing their multifaceted role, which includes equipment provision, technical guidance, lifecycle support, and adaptation to evolving industry needs. When viewed from a non-promotional and informational perspective, the term highlights the importance of specialized knowledge and coordination in supporting reliable vacuum system operation across a wide range of sectors.



Responses